Delegates:
A Method can have one or more parameters of different data types, But what if we want to pass a Method itself as a Parameter? How does C# Handle the Callback Method? The Answer is Delegate. C# Delegates are Similar to Pointers to Function in C or C++. Delegate is a reference type data type and it holds the reference of a Method. All the Delegates are Implicitly derived from System.Delegate Class.
Declaring Delegates:
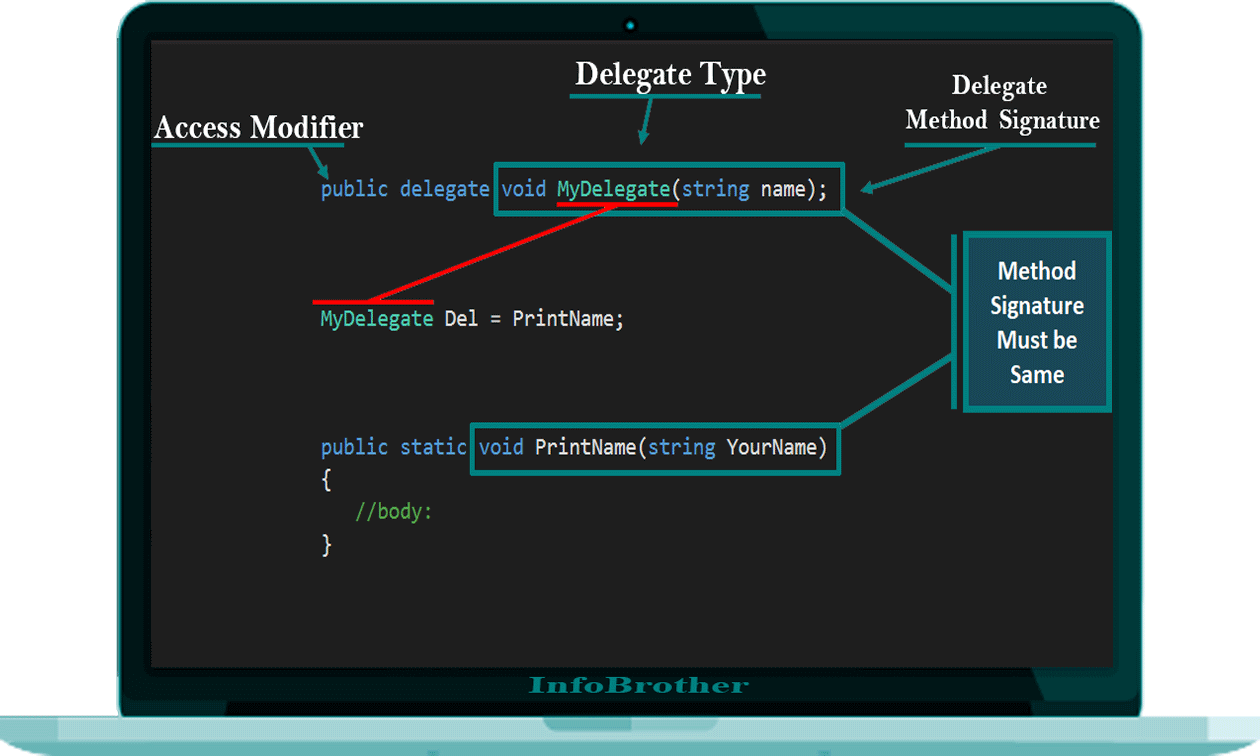
Delegates are used to pass methods as Argument to Other Methods. We Declare Delegate using Delegate Keyword followed by a Method Signature as Shown below.
Access_Modifier delegate Return_Type delegate-name( Parameters);
Delegate declaration determines the Methods that can be referenced by the delegate. a Delegate can refer to a method, which has the same signature as that of the Delegate. For example:
public delegate int MyDelegate( string name);
The Above Delegate can be used to reference any method that has a Single string parameter and return an Int type variable.
Instantiating Delegate:
After Declaring the Delegate, we create the delegate object using New Keyword and be associated with a particular method. When we creating a Delegate, the Argument passed to the New expression is written similar to a method call, but without the Arguments to the method. Consider this example:
public delegate void MyDelegate(string name);
//
//Instantiating Delegate:
MyDelegate Obj1 = new MyDelegate(Method1);
MyDelegate Obj2 = new MyDelegate(Method2);
Let's have an simple example here to understand how this delegates work.
/*Example - Delegates - InfoBrother*/
using System;
namespace Delegaters
{
/*Delegate will return int type, and will
accept only 2 int type parameters: */
public delegate int add(int x, int y);
class Program
{
//method with same Delegate Method Signature:
public static int numbers(int a, int y)
{
return a + y;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
add obj = new add(numbers); //Instantiating Delegate
int val1 = 10;
int val2 = 20;
//using Delegate.
double result = numbers(val1 , val2);
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", val1, val2, result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Delegates:
10 + 20 = 30
Multicast Delegate:
The Delegate can Points to multiple methods. The Delegate that Points to Multiple methods is known as Multicast Delegate. The plus " + " Operator is used to adds a Methods to the delegate object and the Minus " - " Operator is used to remove an existing method from a Delegate Object. consider the Following Example:
/*Example - Multicast Delegates - InfoBrother*/
using System;
namespace Delegaters
{
/*Delegate will return int type, and will
accept only 2 int type parameters: */
public delegate int add(int x, int y);
class Program
{
//method with same Delegate Method Signature:
public static int ADD(int a, int y)
{
return a + y;
}
//method with same Delegate Method Signature:
public static int SUBTRACT(int a, int y)
{
return a - y;
}
//method with same Delegate Method Signature:
public static int DIVIDE(int a, int y)
{
return a / y;
}
static void Main(string[] args) //main method:
{
//Instantiating Delegate
add OBJ;
add obj1 = new add(ADD);
add obj2 = new add(SUBTRACT);
add obj3 = new add(DIVIDE);
int val1 = 20;
int val2 = 10;
//Using Delegates:
OBJ = obj1;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", val1 , val2, OBJ(val1, val2));
OBJ += obj2;
Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1} = {2}", val1, val2, OBJ(val1, val2));
OBJ += obj3;
Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1} = {2}", val1, val2, OBJ(val1, val2));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Multi-casting of a Delegate:
20 + 10 = 30
20 - 10 = 10
20 / 10 = 2

